how do hot air balloons work gas laws
Our pilots are certified experts at steering a hot air balloon using incredible precision to safely give customers an incredible and memorable experience. For a given quantity of gas the pressure P multiplied by the.

Hot Air Balloons And Gas Laws By Emily Taylor By Emily Taylor
A hot air balloon is a balloon used for travel through the air in a basket suspended below a large bag of heated air.

. Thus the heated air inside the balloon is less dense than the cool air outside of the balloon. 1 A hot air balloon stays on the ground or descends when the air inside it is too cool. We can rearrange the Ideal Gas Law PVnRT to calculate the density p of the hot air.
A Hot Air Balloon is an application of Charles Law. How does a hot air balloon work. But molecules are free to escape.
Law provides an explanation of how hot-air balloons work. How to get repeat customers. Obviously if the air is allowed to cools the balloon begins to slowly come down.
Hot Air Balloons By Bhaavi Patel What is a hot air balloon. Before long the hot air inside the balloon is less dense than the cool air that surrounds it. Below you can see liquid nitrogen being poured over a green balloon.
The hot air balloon operates on the principle of Charless Law which states that the volume of a gas increases with temperature. The law that explains how hot air balloons work is the Charless Law. Modern hot air balloons heat the air by burning propane the same substance commonly used in outdoor cooking grills.
When the density of the balloon decreases to be less than the density of the outside air the balloon rises. Hot air is therefore less dense than cold. Created by Gabriel Lee Brian Su and Andrew Wang 5th period Schnell.
1 Buoyancy 2 From liquids to gases 3 Hot air balloon 4 Outlook Buoyancy In the article Buoyancy the physical cause of the buoyant force were explained in detail. P RTPM where M is the molar mass of the gas The molar mass of air is about 29 gmol. The cold liquid nitrogen cools the air inside the balloon.
When you fill the balloon with hot air it will eventually fill up all the way. If the balloon were sealed pressure would soon build to the bursting point. The balloon thus rises.
-Now when you keep heating the air and you raise the temperature this means that the volume will have to increase as well. Just as an object less dense than water rises to. The intake hose runs down to the bottom of the cylinder so it can draw the liquid out.
Heating the air increases the speed of its gas particles in air so they move faster and spread out according to kinetic molecular theory as. - A hot air balloon works with the Charles Law. ρ PMRT where M is the molar mass of the gas The molar mass of air is about 29 gmol.
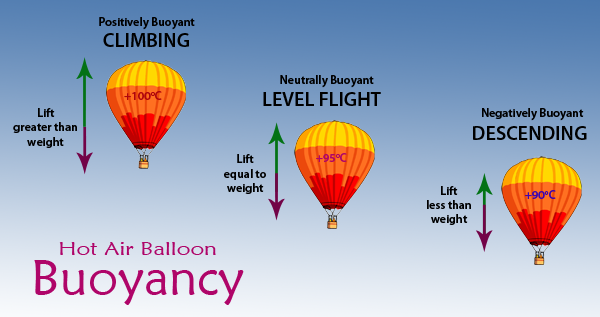
If a gas expands when heated then a given weight of hot air occupies a larger volume than the same weight of cold air. When the density of the balloon decreases to be less than the density of the outside air the. In this case the weight of the balloon blue arrow is greater than the lift red arrow.
Hot air is therefore less dense than cold air. The Ideal Gas Law states that the Pressure times the Volume is equal to the number of molecules times the gas constant R times the Temperature. That air begins to rise and since its trapped in the balloon it lifts the hot air balloon into the sky.
If gas expands when it is heated a given weight of hot air occupies a larger volume. If a gas expands when heated then a given weight of hot air occupies a larger volume than the same weight of cold air. This will be illustrated in the following by the example of a hot air balloon.
- However this reaction is also connected to the Charles Law. This relationship between the temperature and volume of a gas which became known as Charles law provides an explanation of how hot-air balloons work. The Ideal Gas Law governs and all gases air is a gas.
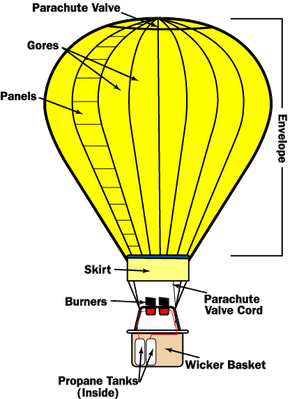
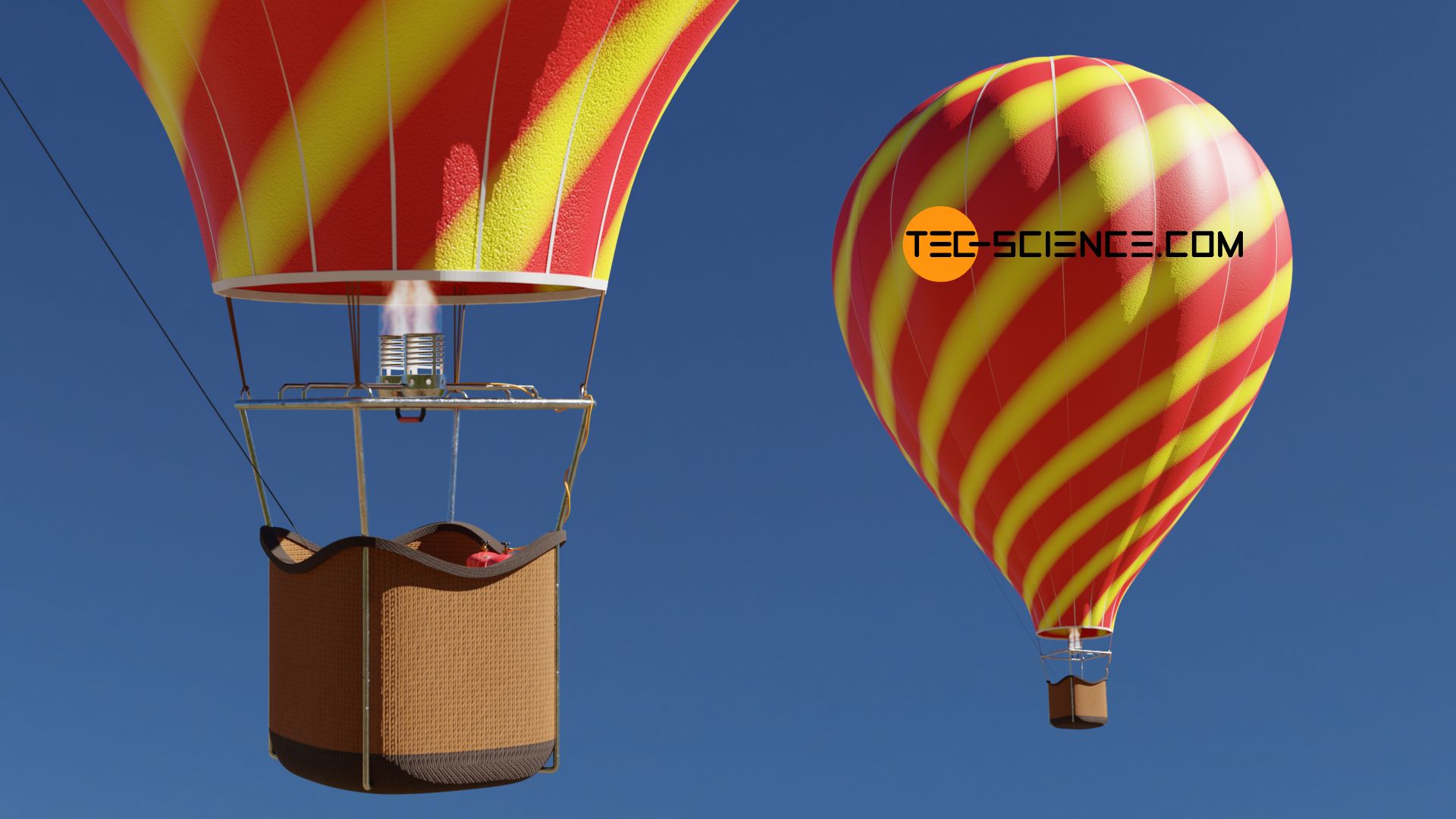
The fuel used heats the air inside the balloon. By heating the air inside the balloon with the burner it becomes lighter than the cooler air on the outside. This law is a mathematical relationship between the volume pressure and temperature of a gas.
PV nRT To figure out why hot. - The gas that is released into the bag is hot due to the reaction causing the bag to fill or inflate - Since the gas is hot it expands rapidly filling the airbag quickly. Sometimes if you think of it in this equation it is a little easier to understand.
Ever since the third century BC it has been known that an object floats when it weighs less than the fluid it displaces. The propane is stored in compressed liquid form in lightweight cylinders positioned in the balloon basket. Hot air balloons work because hot air rises.
In order to make a hot air balloon rise heat is added to the air inside the balloon. The hot air is less dense than cool air is due to the Ideal Gas Law. Much and this is why hot air balloons are so huge -- to lift 1000 pounds you need about 65000 cubic feet of hot air.
How to schedule fewer meetings and get more done. As the air in the balloon is heated by a small flame the balloon expands becoming less dense than the surrounding cool air. 2 When the air inside is a bit hotter the balloon floats at a steady height because the lift force and weight are now the same.
Is a hot air balloon Charles Law. Conversely the volume of a gas will shrink if its temperature decreases. We can rearrange the Ideal Gas Law PV nRT to calculate the density ρ of the hot air.
This causes the balloon to float upwards as if it were in water. When the lift and weight are the same the balloon floats. As air inside the balloon heats up the molecules move faster and faster.
This relationship between the temperature and volume of a gas which became known as Charles law provides an explanation of how hot-air balloons work. Buoyancy in gases Buoyant forces act not only in liquids but also in gases. Using Prezi Video for virtual sales presentations that convert.
The balloon has a fixed volume so the extra volume flows out of the hole in the bottom of the balloon. When the weight is greater than the lift the balloon descends. It is used for recreational activities but many scientific principles apply to it.
- As you keep heating the air it gets bigger and since the balloon can only hold so much air it starts to let out small amounts of air. And that is how buoyancy causes balloons to work. As long as the lift is greater than the weight the balloon rises.
Making the volume go up as it fills the bag. This says that the density of the air decreases as itse temperature increases. How Hot Air Balloons Work.
Gas laws and how hot air balloons work Chapter 5 covers gas lawshow are they relevant to how hot air balloons work Gas laws and sports how to throw a curve ball how do gasses impact the flight of a football soccer ball baseball which is a pitchers versus hitters park and way with respect to gasses and gas laws etc. If you are interested in learning more about how hot air balloons work or would like to schedule a hot air balloon tour in Temecula contact Compass Balloons today by calling 760 704-7407.

Everything About Hot Air Balloon In My View Physics In My View

10 4 Buoyancy Volume Temperature And Pressure Of Gases A Hot Air Balloon Floats Because The Air Inside Is Less Dense Than The Air Outside The Balloon Ppt Download

Pin By Quantazia Merchant On Final Chemistry Project Chemistry Projects Charles Law Chemistry

Give Possible Explanation Of How Hot Air Works By Charles Law Brainly In

Chemistry Chapters 12 13 The States Of Matter And Gas Laws Ppt Download

Charles S Law Examples Chemistrygod

Calculating Molar Volume Density From The Ideal Gas Law Chemistry Jove

How Does A Hot Air Balloon Work Buoyancy In Gases Tec Science

Charles Law And Gay Lussac S Law Let S Talk Science
Section 2 Gas Behavior Objective What Gas Law Explains Why This Ppt Video Online Download

How Do Hot Air Balloons Work By Sandra Dvoyrin

The Gas Laws Hot Air Balloons By Ashley Wagnblas
How Hot Air Balloons Work Howstuffworks

How Does A Hot Air Balloon Work Buoyancy In Gases Tec Science

Charles Law And Gay Lussac S Law Let S Talk Science

Combined Gas Law Ck 12 Foundation

How Hot Air Balloons Work Gas Laws

Gas Laws Hot Air Balloons By Jonathan Dauterman On Prezi Next